Bermuda Plans Full Transition to Blockchain Infrastructure: National Economy Goes Digital

January 20, 2026 - In a move that signals a fundamental shift in how governments are thinking about financial infrastructure, Bermuda has announced an ambitious plan to transition its entire economy to blockchain-based infrastructure. This is not a pilot program or a limited experiment; this is a national commitment to reimagine how a modern economy operates in the digital age. The initiative includes stablecoin payments for government services, tokenization of assets for banks, and comprehensive digital literacy programs for its citizens [1].
Bermuda's decision to embrace blockchain infrastructure is not born out of desperation or a lack of alternatives. Rather, it reflects a clear-eyed recognition that blockchain technology offers significant advantages over traditional financial infrastructure: lower costs, faster settlement, greater transparency, and improved accessibility. The government has partnered with leading blockchain companies, including Circle and Coinbase, to implement this transformation [1]. These are not fringe players; these are among the most respected and well-capitalized companies in the blockchain space.
"Bermuda is positioning itself as a laboratory for the future of finance," a recent report from a leading fintech publication noted. "By embracing blockchain infrastructure at a national level, Bermuda is not just improving its own financial system; it is demonstrating to the world what is possible when governments and technology companies work together to reimagine money and finance."
The Bermuda initiative encompasses several key components. First, the government is implementing stablecoin payments for government services, allowing citizens to pay taxes, fees, and other obligations using digital currencies. This is a powerful statement about the government's confidence in stablecoins as a reliable medium of exchange. Second, Bermuda is working with its banking sector to tokenize assets, creating digital representations of traditional financial instruments on the blockchain. This will enable faster settlement, lower costs, and greater transparency in financial transactions.
| Bermuda Blockchain Initiative | Component | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Stablecoin Payments | Government services and payments. | Demonstrates government confidence in digital currencies. |
| Asset Tokenization | Banks tokenizing traditional financial instruments. | Enables faster settlement and lower costs. |
| Digital Literacy Programs | Comprehensive education for citizens. | Ensures broad adoption and understanding of blockchain technology. |
| Partnership with Circle & Coinbase | Leading blockchain companies supporting implementation. | Brings world-class expertise and resources to the initiative. |
Third, and perhaps most importantly, Bermuda is implementing comprehensive digital literacy programs to ensure that its citizens understand and can effectively use blockchain-based financial infrastructure. This is a critical component that is often overlooked in discussions of blockchain adoption. Technology is only useful if people understand how to use it. Bermuda's commitment to digital education suggests that the government is serious about ensuring that the benefits of blockchain infrastructure are broadly shared across society.
The Bermuda initiative has profound implications for the broader adoption of blockchain technology and stablecoins. For years, skeptics have argued that blockchain technology is too complex, too risky, and too unproven for mainstream adoption. Bermuda's decision to embrace blockchain infrastructure at a national level is a powerful counter-argument to these concerns. If a stable, well-governed jurisdiction like Bermuda is confident enough to transition its entire economy to blockchain infrastructure, then the technology has clearly matured beyond the experimental stage.
For traders, quants, and investors, Bermuda's blockchain initiative is a significant positive signal for the future of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology. It suggests that governments are beginning to recognize the value of blockchain infrastructure and are willing to invest in its development. As more governments follow Bermuda's lead, the demand for blockchain infrastructure, stablecoins, and related services will accelerate. The companies and tokens that enable this transition are likely to see significant appreciation as the market recognizes the long-term value of these technologies.
The Bermuda initiative also has implications for the regulatory landscape. By embracing blockchain technology at a national level, Bermuda is sending a clear message that it welcomes blockchain innovation and is committed to creating a regulatory environment that supports the development of blockchain-based financial infrastructure. This could attract blockchain companies and entrepreneurs to Bermuda, creating a virtuous cycle of innovation and economic growth.
References
[1] Bermuda Plans to Fully Transition Its Economy to Blockchain Infrastructure
Related Articles
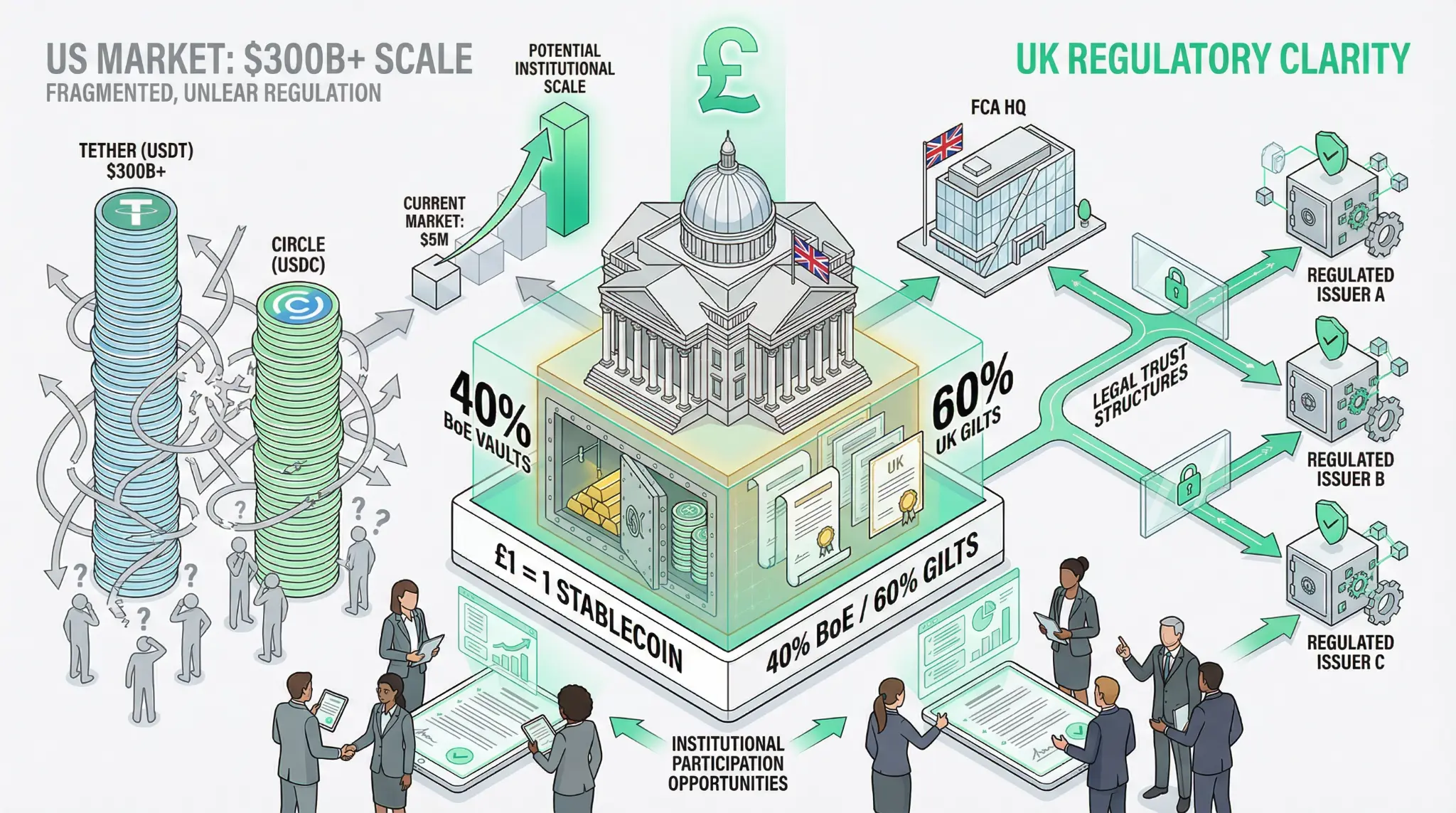
FCA Declares Sterling Stablecoins Top Priority: UK Sets Clear Regulatory Framework While US Remains Fragmented
January 26, 2026 - In a strategic move that positions the United Kingdom as a potential leader in stablecoin regulation, the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) has declared sterling-backed stablecoins a top priority for 2026, while simultaneously working with the Bank of England to establish a comprehensive regulatory framework [1]. The UK's approach stands in sharp contrast to the fragmented regul
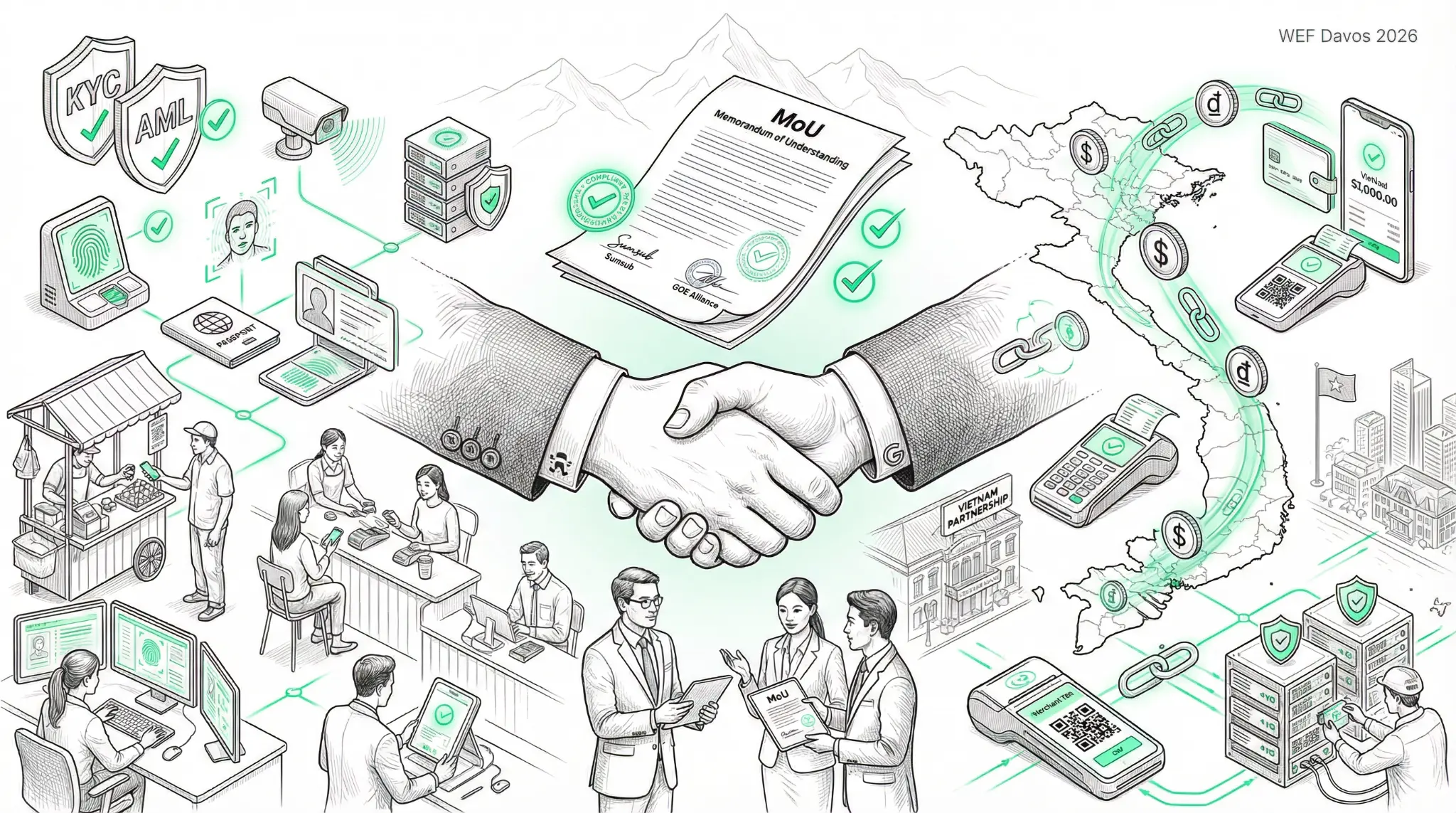
Sumsub and GOE Alliance Sign MoU at Davos: Compliant Crypto Payments Coming to Vietnam
Sumsub and the GOE Alliance have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) at the World Economic Forum in Davos to support the development of compliant crypto payment infrastructure in Vietnam. This partnership represents a convergence of compliance expertise, regulatory understanding, and market opportunity that could accelerate the adoption of cryptocurrency payments across Southeast Asia.
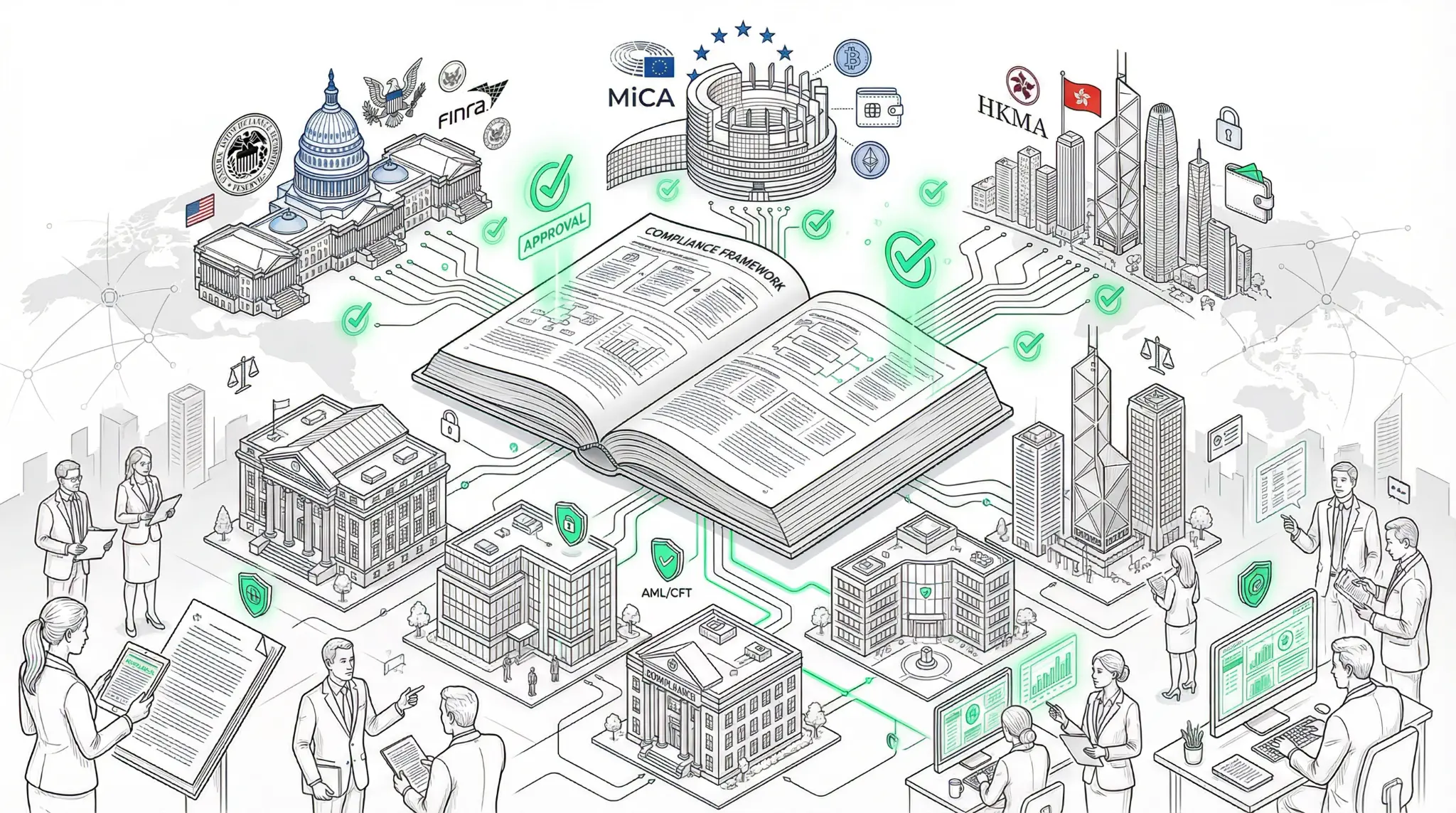
Elliptic Releases Comprehensive Stablecoin Compliance Playbook: The Regulatory Framework is Finally Here
Elliptic, a leading blockchain compliance firm, has published a comprehensive compliance playbook for stablecoin issuers and financial institutions. The playbook outlines the regulatory frameworks now in place across the US, EU, and Hong Kong, and provides detailed guidance on anti-money laundering and counter-financing of terrorism measures, as well as sanctions compliance requirements.
